Generative AI Use Cases for Companies: From Core Capabilities to Operational Impact part 1
Explore how generative AI is transforming company operations across industries. Understand its core capabilities, the taxonomy of use cases, and the practical impact on business processes from a first-principles perspective.
Author
D Team
Aug 31, 2024
Generative AI Use Cases for Companies: From Core Capabilities to Operational Impact
Generative AI, an advanced subset of artificial intelligence, is redefining how companies operate, innovate, and compete. Its unique ability to generate new content, ideas, and solutions from existing data opens the door to unprecedented possibilities across industries. This article delves into generative AI from a first-principles perspective, examining its fundamental capabilities, a structured taxonomy of use cases, and its transformative impact on company operations.
Understanding Generative AI from First Principles
To fully appreciate the potential of generative AI, it's essential to understand its underlying mechanics. Unlike traditional AI models that classify data or make predictions, generative AI models, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Transformer-based models like GPT, create new data similar to what they have been trained on. This capability is powered by three core components:
Data Synthesis: Generative AI synthesizes new data points from existing data, offering unique possibilities in data augmentation, creating synthetic data for model training, and simulating scenarios.
Pattern Recognition and Learning: At the core, generative AI models excel at recognizing complex patterns in data and learning from them to generate new outputs. This includes natural language, images, audio, and even complex simulations.
Autonomous Creativity: Beyond mere data manipulation, generative AI introduces an element of creativity and innovation, producing results that were not explicitly programmed, such as creating new designs, composing music, or drafting coherent narratives.
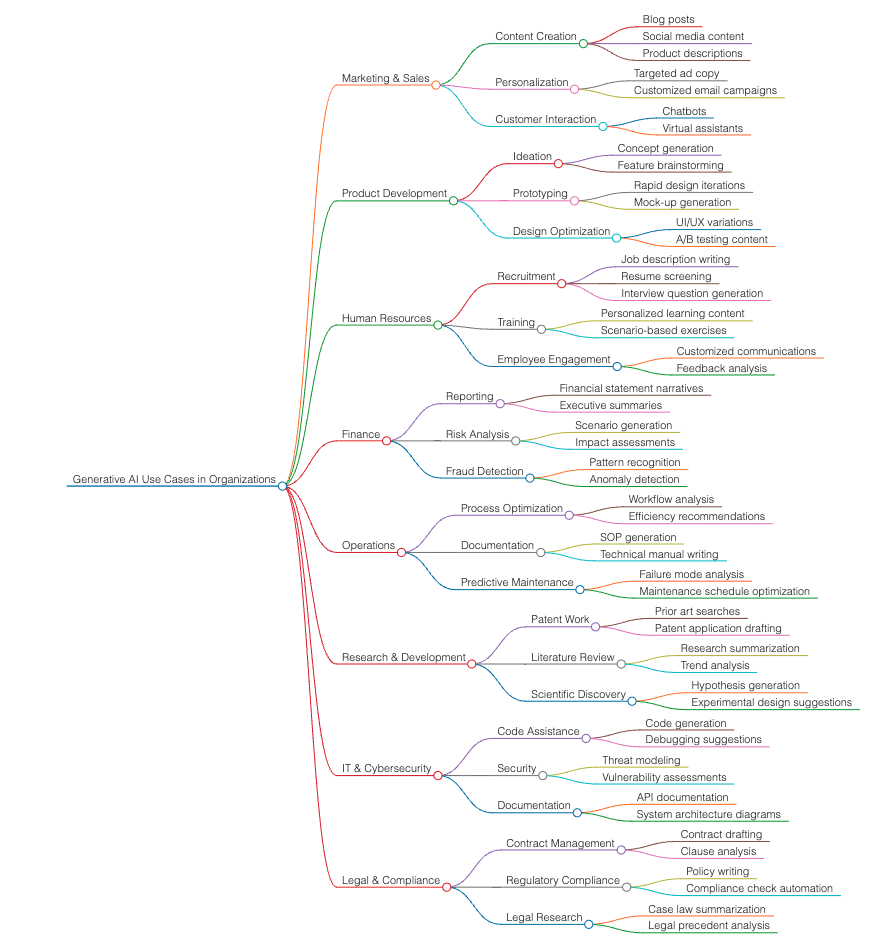
Taxonomy of Generative AI Use Cases
The potential applications of generative AI can be systematically categorized into several domains based on their fundamental capabilities. Here is a taxonomy of generative AI use cases that companies can leverage:
1. Content Creation and Personalization
Marketing and Advertising: Generative AI can craft personalized marketing content at scale. It can generate tailored emails, social media posts, and advertisements based on user behavior and preferences, significantly improving engagement rates.
Automated Copywriting and Design: Tools like GPT and DALL-E can produce engaging copy and creative designs, reducing the need for extensive human involvement in repetitive creative tasks. This capability extends to product descriptions, blog posts, and visual content generation.
Dynamic Web Content: Generative AI can create dynamic, personalized web content that adapts in real-time to user interactions. This enhances user experience, potentially increasing conversion rates.
2. Product Development and Innovation
Design Automation: In industries such as fashion, architecture, and automotive, generative AI can automatically design products based on certain parameters, saving time and enhancing creativity. For example, Nike and BMW have used generative AI to design more efficient footwear and vehicle components, respectively.
Prototyping and Testing: Generative models can simulate different scenarios and generate prototypes for products, allowing companies to explore more ideas faster and at a lower cost.
Drug Discovery and Material Science: In pharmaceuticals, AI-driven generative models help design new molecules and drugs by predicting their interactions, speeding up the traditionally lengthy R&D process.
3. Operations and Efficiency Enhancement
Supply Chain Optimization: Generative AI can forecast demand and optimize supply chain operations by generating predictive models that adapt to changing market conditions, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Process Automation and Improvement: Companies use generative AI to identify inefficiencies and generate optimal workflows. This includes optimizing routes for logistics companies or automating scheduling for manufacturers.
Human Resources and Recruitment: AI-generated personality assessments, interview questions, and even recruitment bots are becoming mainstream, allowing companies to screen candidates more effectively and with fewer biases.
4. Customer Interaction and Support
AI-Powered Customer Service Agents: Generative AI chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 customer support, handling inquiries, complaints, and feedback with high accuracy and contextual understanding.
Personalized Customer Experiences: Beyond text-based support, generative AI can customize entire customer experiences. For instance, AI-generated recommendations in e-commerce or streaming services enhance user satisfaction and retention.
5. Strategic Decision-Making and Forecasting
Scenario Generation for Business Strategy: Generative AI can simulate various market scenarios and help companies understand potential outcomes of different strategies. This is particularly valuable in dynamic markets where conditions can change rapidly.
Financial Modeling and Risk Assessment: Generative AI can generate financial forecasts and risk models, providing valuable insights for investment and strategic planning.
Fundamental Capabilities: How Generative AI Supports Company Operations
Integrating generative AI into business operations is not just about deploying advanced technology—it's about leveraging its core capabilities to fundamentally enhance how companies operate. Here are some fundamental ways generative AI impacts company operations:
Scalability: Generative AI allows businesses to scale their creative and operational efforts without a linear increase in cost or manpower. For instance, a single AI model can generate thousands of personalized marketing materials at a fraction of the time and cost.
Efficiency and Speed: By automating routine and complex tasks, generative AI significantly reduces the time required for processes like content creation, prototyping, and customer support, enabling faster decision-making and time-to-market.
Innovation Potential: Generative AI introduces new possibilities for innovation, from discovering new product ideas to creating new business models. It opens avenues for companies to explore and capitalize on previously untapped opportunities.
Enhanced Customer Experiences: The ability to generate personalized and dynamic customer interactions helps businesses build deeper relationships with their customers, improving satisfaction and loyalty.
From a Research-Driven Perspective: Derivative GPT Viewpoint
From a research-driven perspective, the adoption of generative AI presents both opportunities and challenges for companies. The benefits are clear—enhanced efficiency, innovation, and customer experience—but they come with considerations around ethical use, data privacy, and potential biases. As companies increasingly rely on AI-generated outputs, it is vital to maintain human oversight to ensure that these technologies are applied responsibly. Ongoing research and development are essential to refine these models, improve their accuracy, and mitigate any potential risks associated with their deployment.
Check part 2 for following
Conclusion
Generative AI is not just a technological advancement; it represents a paradigm shift in how companies operate and innovate. By understanding its core capabilities and applying them across various operational domains, companies can unlock new value and stay competitive in an increasingly digital world. As generative AI continues to evolve, those who adapt early and strategically will lead the next wave of digital transformation.